A clandestine research facility is creating a highly accurate “quantum clock” that could have a significant impact on British intelligence.
planes.
It will also ‘enhance the accuracy of advanced weapons’ such as guided missiles and provide British computer experts with an edge over online adversaries like cyber criminals.
This clock will be precise to the point that it will lose less than one second over billions of years, enabling scientists to measure time at a scale they’ve never reached before.
It is the UK’s first-of-its-kind device and is expected to be deployed on military operations within the next five years, as stated by the Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (DSTL).
‘This milestone project marks a major breakthrough in the UK’s cutting-edge quantum technology capabilities,’ stated DSTL chief executive Paul Hollinshead.
‘The data collected will not only influence the future defense efforts but also serves as a notice to industry and academia of our commitment to exploring quantum technologies for enhanced security and operational resilience.’
Quantum clocks utilize quantum mechanics, the branch of physics governing atomic and subatomic behavior, to record time with unmatched precision by monitoring energy variations within individual atoms.

Current quantum clocks are even more accurate than the “atomic clocks”, of which there are approximately 400 already in operation globally.
The UK has an atomic clock at the National Physical Laboratory in London, but this new quantum clock will be its first one.
Nick France, Sectigo’s Chief Technology Officer, stated: ‘A quantum clock is a type of atomic clock – essentially a highly precise timekeeping device.
‘Atomic clocks operate by quantifying the resonant frequency of atoms. Quantum clocks, however, measure minute energy variations, known as ‘quantum fluctuations’, in these atoms, resulting in enhanced accuracy even surpassing that of atomic clocks.’
‘Currently, atomic clocks possess exceptional accuracy. However, a quantum clock has an even higher level of accuracy, where only a single second would be lost over the course of billions of years of operation.’
The British quantum clock will be the UK’s first domestically produced device of its kind, according to the UK government, although it won’t be the first of its kind globally.
In 2010, the University of Colorado at Boulder collaborated with the United States’ National Institute of Standards and Technology to create a quantum clock.
However, key barriers to deploying quantum clocks are their scale – current models come in a van or in a car trailer and are approximately 1,500 litres in volume.

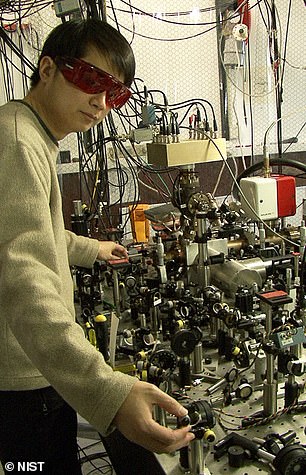

Like most quantum machinery, quantum technology is also sensitive to environmental factors, such as heat and air molecules, which restrict their movement between different locations.
“Quantum clocks are not tiny, like the ones you find on watches or alarm clocks,” France added.
In current implementations, these devices can be quite large, approaching the size of a whole room.
However, ongoing advancements in technology are expected to shrink the size of these devices, making them more compact and mobile.
In addition to establishing ultra-precise time standards, quantum clocks could revolutionize global navigation systems by enhancing satellite communications and aircraft navigation.
According to DSTL, the quantum clock is expected to enable more precise and self-contained navigation systems, thereby lessening reliance on GPS satellites that are susceptible to interference or destruction in conflict situations.
This technology will enhance communication systems, including secure networks used by the military that must be precisely synchronized in time. It will also increase the accuracy of sophisticated weapon systems, like guided missiles, which need precise timing to determine trajectories and execute attacks.
Furthermore, British Armed Forces will enjoy a distinct advantage over adversaries in “timing-critical operations”, including cyber warfare, where seconds can indeed make a critical difference.

Cyber warfare refers to the actions by a nation or international organization to attack and try to harm another country’s computers or information networks.
France stated to MailOnline: “Accurate timekeeping is crucial for governments and military organizations as it enables precise navigation of aircraft and vessels using GPS or similar technologies, as well as guiding military systems like missiles.”
Secure communication is equally important for both military and civilian purposes.
Access to secure and precise timing is crucial to maintain the integrity of government and military communications.
‘But these highly accurate clocks also have practical uses in civilian settings and in enhancing the overall security of internet connections, including safeguarding your personal data as it is transmitted across the global network.’
Organizations and governments globally are eager to capitalize on the vast possible advantages that the striking influence of quantum technology can offer.
Google in the past month revealed a new quantum computing chip, which it stated could accomplish a given task in mere minutes, whereas leading supercomputers would require an impressive 10 septillion years.
In the future, a chip of this kind could potentially power a “commercial” quantum computer, which would be available for purchase by the general public, and could be used in research labs, offices, and even at home.
and discover lifesaving drugs.





